Mathematical Models, Elements and Electric
Circuits
A
model is an object or pattern of objects
or an equation that represents an element
or circuit.
-
Engineers use models to represent the
elements of any system including electric
circuit.
-
Models are generated for manufactured
elements and devices in order to facilitate
understanding and establish the operating
characteristics of the elements and
devices.
In
this unit, we will construct model of elements
and then interconnect them to form a circuit
model.
Many
of today’s systems, ranging from chemical
plants to automobile, require some form
of electronic or computer control for proper
operation. Such control systems rely heavily
on mathematical foundations of electric
circuits, logic theory, and system theory.
In
our study of electric circuits, we make
a number of simplifying assumptions. First,
we assume that the important characteristics
of circuits can be grouped together in lumps
or separate blocks, connected together by
ideal conductors (wires). This approach
is called lumped element circuit
modeling and is used in circuit
analysis.
In
this unit, we are concerned with simple
mathematical models of electrical circuit
elements.
Elements are the basic building blocks of
an electric circuit.
-
There are two types of elements found
in electric circuits: passive
elements and active
elements.
-
An active element is capable of generating
energy while a passive element is not.
-
Examples of passive elements are resistors,
capacitors, and inductors.
-
Typical active elements include power
sources, transistors, and operational
amplifiers.
There
are three passive circuit elements that
usually are assumed as single-valued in
circuit analysis:
-
Resistor
- Inductor
- Capacitor
They will be discussed later in following
sections. These three passive elements vary
in the way in which the voltage across is
related to the current through each of the
elements.
The commonly used symbols for these
three elements are given in Figure 3.
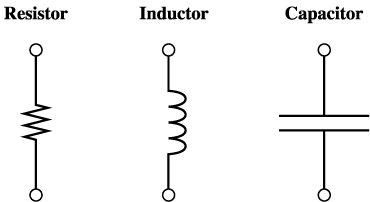
Figure
3 Passive Circuit Elements
|