What is Ohm’s
Law?
Type your answer in the box below:
Ohm’s
law is the main basic electrical law
and defines the resistance of a device
to the flow of electrons. It was named
after the German physicist GEORG
SIMON OHM (1787-1854).
Ohm’s law deals with the relationship
between voltage and current in a load.
This relationship states that: the potential
difference v
across a load is proportional to the
current i
through it. The constant of proportionality
is called the resistance R.
Ohm's law may be used to solve simple
circuits. A simple circuit means one
which contains one source of voltage,
and one potential drop i.e., a place
where potential energy decreases.
The sum of the voltages around a complete
circuit is zero.

Ohm’s Law Chart
Figure 5.1 shows
a collection of circles to help you
remember Ohm’s law. To recall
the equation for any quantity, just
cover the quantity on the circle.
Then read the remaining quantities
as the equation.
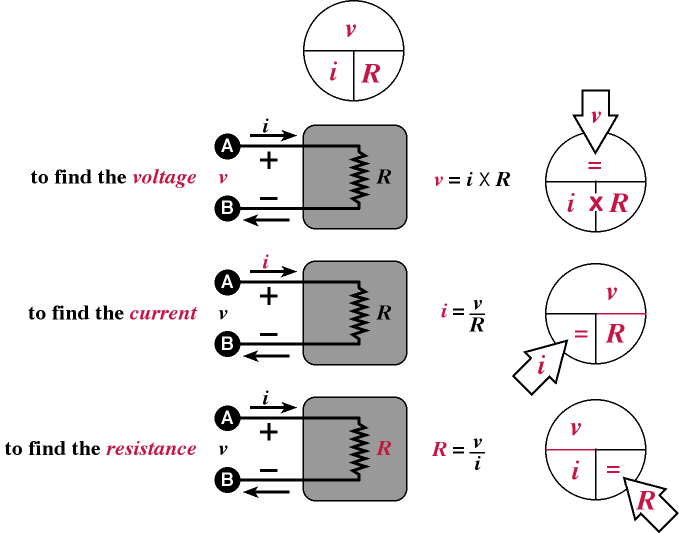
Figure 5.1 Ohm’s
Law Circle
|